- Red Hat Community
- :
- Discuss
- :
- Containers, DevOps & OpenShift
- :
- Re: JFrog Xray
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 8,229 Views
JFrog Xray
Hello Red Hat Community,
I am keen on integrating JFrog Xray into our development environment that's based on OpenShift. Before proceeding with this integration, I'd like to first test it out locally to understand its workings and potential benefits.
Could anyone here provide insights or share experiences regarding the integration of JFrog Xray with OpenShift? Any guidance or best practices would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you in advance!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 6,102 Views
@nuri Can you please check if the below link help?
https://cloud.redhat.com/blog/cloud-devops-with-openshift-and-jfrog
https://jfrog.com/blog/protect-your-containerized-microservices-on-openshift-using-jfrog-xray/
Regards,
Wasim
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 6,100 Views
Hello @nuri !
Thanks for reaching out!
Check out the video below where Jeff Fry of JFrog and Phillip Lamb of Red Hat demonstrates the ease of supporting DevOps with a fully-fledged pipeline in a cloud and source control, CI server, artifact repository, security vulnerability, license compliance scanner, Docker registry, Helm repository, runtime, and OpenShift, tracing, and monitoring tools :
Check this catalog for Jfrog Xay and Openshift : https://catalog.redhat.com/software/container-stacks/detail/5ecabc9ab58ac77d83eb98e3
Refer this for best practices : https://jfrog.com/help/r/get-started-with-the-jfrog-platform/onboarding-best-practices-jfrog-artifac...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 6,037 Views
This is the answer from GPT4
Integrating JFrog Xray into your OpenShift environment can help you to enhance your security and compliance measures by scanning your artifacts for vulnerabilities and license compliance issues. Here's a general approach to testing it out locally before a full-scale integration:
### Understanding JFrog Xray:
JFrog Xray is a universal software composition analysis (SCA) solution that scans binary artifacts and their metadata, containers, and software packages to identify security vulnerabilities and license compliance violations.
### Prerequisites:
- Ensure you have an OpenShift cluster running locally (using MiniShift or Red Hat CodeReady Containers for example) or access to a development cluster.
- Set up a JFrog Artifactory instance which Xray will integrate with, as it requires an artifact management platform to function.
- Obtain the JFrog Xray package suitable for your environment.
### Steps for Local Testing:
1. **Install JFrog Artifactory**: Xray works alongside Artifactory to scan artifacts. If you haven't already, you should first set up a JFrog Artifactory instance. You can use a Docker container for local testing.
2. **Install JFrog Xray**:
- You can run Xray as a Docker container or install it in a similar manner to Artifactory.
- Ensure that the Xray version is compatible with your Artifactory version.
3. **Integrate Artifactory with Xray**:
- Within the Xray UI, connect to your Artifactory instance.
- Set up watches and policies in Xray to define which repositories and builds need to be scanned.
4. **Deploy JFrog Xray on OpenShift**:
- Use the OpenShift CLI (`oc`) to deploy Xray onto your OpenShift cluster.
- You'll likely need to create a new project and define resources such as pods, services, and routes.
- Configure persistent storage for Xray, as it requires a place to store its data.
- Ensure the necessary security contexts are set for the service to run properly.
5. **Configure Security and Compliance Policies**:
- Set up the security policies in Xray to define how it should respond to vulnerabilities.
- Define compliance policies to ensure that license requirements are met.
6. **Scan Your Artifacts**:
- Once Xray is integrated with Artifactory and your policies are in place, upload an artifact to Artifactory and see how Xray scans it.
- Review the scan results and understand the vulnerability and compliance data it provides.
### Best Practices:
- **Isolate Environments**: When testing locally, ensure that your test environment is isolated from production to prevent any unintended disruptions.
- **Automate**: Look into automating the deployment process using OpenShift templates or operators to make it easier to replicate in other environments.
- **Security**: Make sure that access to Xray is secured and that it operates under the principle of least privilege.
- **Monitoring and Logging**: Configure monitoring and logging to track the health and performance of the Xray service.
- **Disaster Recovery**: Have a plan for backing up Xray’s data and configuration for disaster recovery purposes.
### After Local Testing:
After you are satisfied with local testing, consider the following for a broader deployment:
- **Scale Appropriately**: Evaluate the resource requirements for Xray under load and adjust your OpenShift deployment accordingly.
- **CI/CD Integration**: Integrate Xray scans into your CI/CD pipelines to automate the scanning of artifacts during the development process.
- **Documentation and Training**: Document the integration process and train your team on how to use Xray effectively.
Remember that local testing is just the first step. Once you move to staging or production, you'll need to consider high availability, redundancy, and real-time monitoring to ensure that Xray functions well within your OpenShift environment.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,934 Views
I wont recommend anyone to apply answers from AI to any environment for any technical solution / workaround - unless it is an official documentation or a technical blog.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 6,019 Views
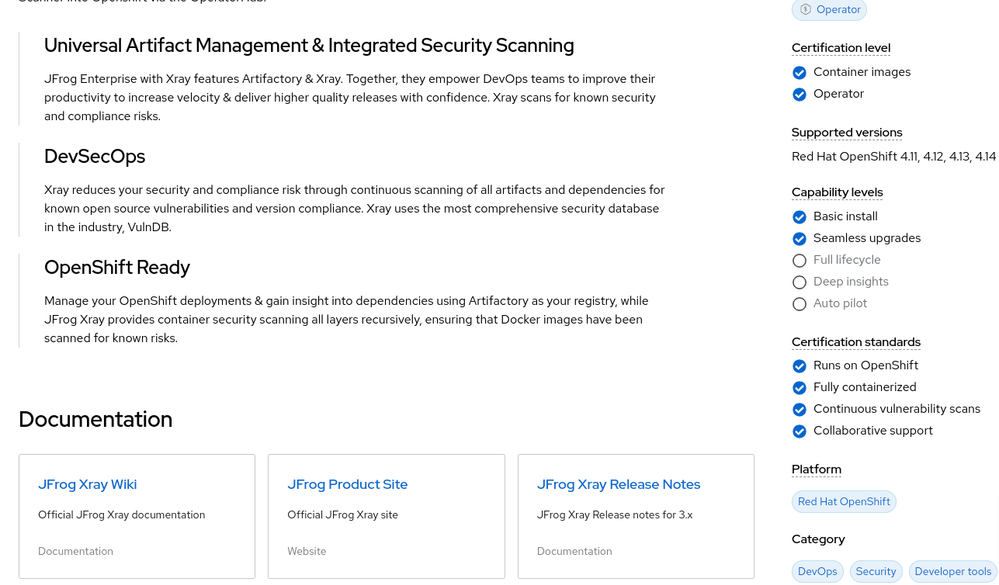
You can make use of the JFrog Xray Operator.
You may refer the following documentations for assistance.
Xray Integration with Red Hat Certified Open Shift Operator • JFrog Integrations Documentation • Rea...
Jfrog Xray - Containerized Product - Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,707 Views
Thank you for your inputs @aneez004 !
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,703 Views
Thanks for sharing @aneez004
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,693 Views
For me it was a little complicated at the beginning, but I found this documentation very useful, I hope it helps you
https://github.com/jfrog/JFrog-Cloud-Installers/blob/master/Openshift4/README.md
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,691 Views
+1
Red Hat
Learning Community
A collaborative learning environment, enabling open source skill development.