- Red Hat Community
- :
- Red Hat Academy
- :
- Forum
- :
- Re: DO188 error in Chapter 6, Section 1
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 2,030 Views
DO188 error in Chapter 6, Section 1
In DO188, chapter 6, section 1, there is a mistake in how a command's option works:
That's not what the -n option does with the ss command. It does not show, or not, IP address(es). Instead, it shows a service's port number (if used) or "friendly name," if not used. Per the man pages:
Proof:
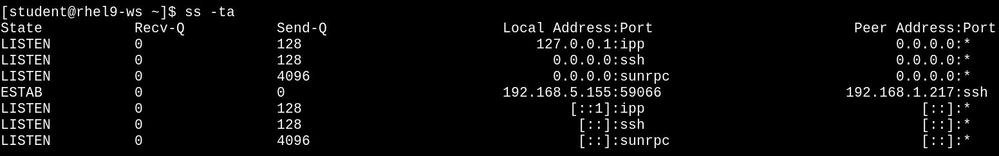
Without the -n option, "friendly" service names are seen, such as ssh, ipp, etc. Note that the 192.168.5.155 IPv4 address has a cononical name (and an alias, too), which is not shown.
With the -n option, "friendly" service names are not seen. Instead, the port numbers are, such as 22, 631, etc. Note that none of the IPv4 (or IPv6) addresses have changed.
Estrella Mountain Community College
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 2,022 Views
Hello @Tracy_Baker !
I dont think " ss -n " prevent ss from displaying IP addresses. It simply tells ss not to try to resolve the IP addresses to service names.
I think it is useful for troubleshooting network issues, as it can help you to identify specific ports and addresses that are causing problems.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 1,981 Views
(Yes, the ss command is very useful when troubleshooting network issues.)
Before I write the rest of this, the same problem exists in the 6.2 guided exercise:
"resolve the IP addresses to service names"
IP addresses and service names are two different things.
They are related inasmuch that they can be used together to create a socket. (i.e.: 192.168.1.1:22 [without -n] or 192.168.1.1:ssh [with -n])
An IP address is, of course, the logical address for a system. They can be mapped to cononical names, aliases, FQDNs, etc.
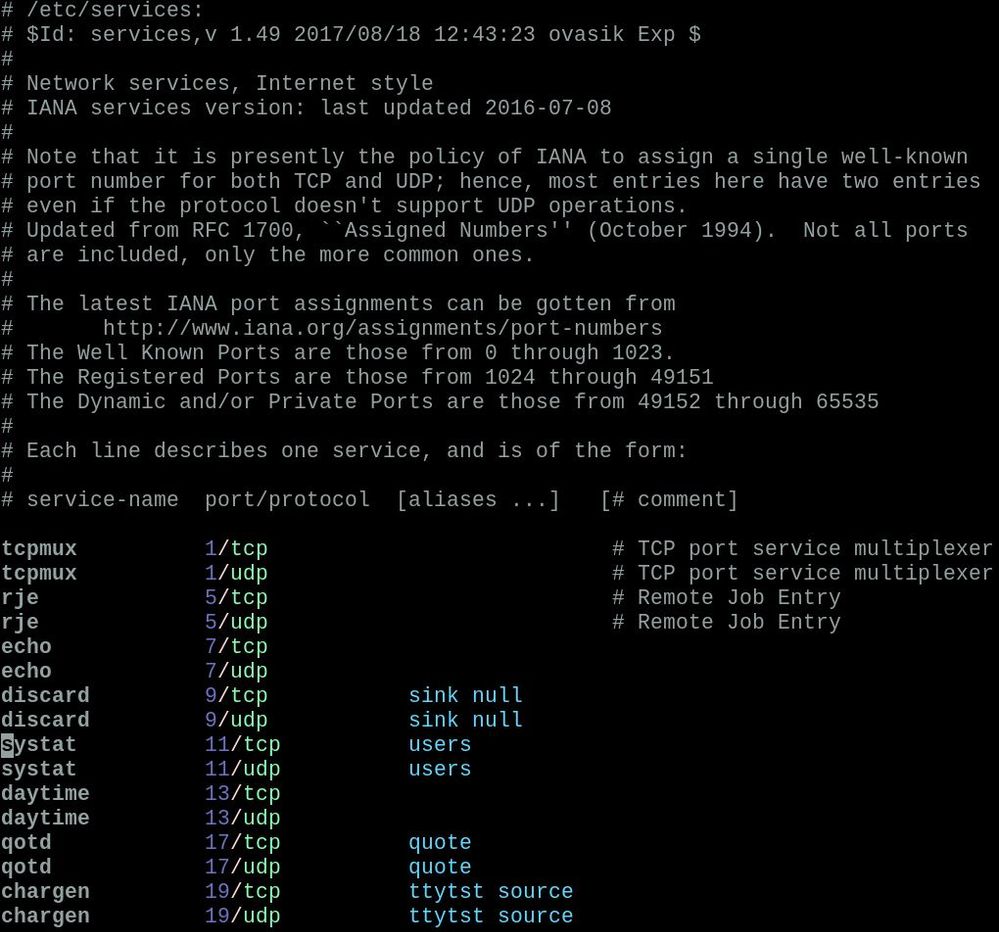
Service name refers to the "friendly name" (the network protocol, in most cases) for a port number. For example, the service name for port 22 is ssh, port 80 is http, port 443 is https, etc. These port number to service name translations can be seen in /etc/services. If you look, you'll see that there are no IP addresses in the file, nor are they mentioned.
...
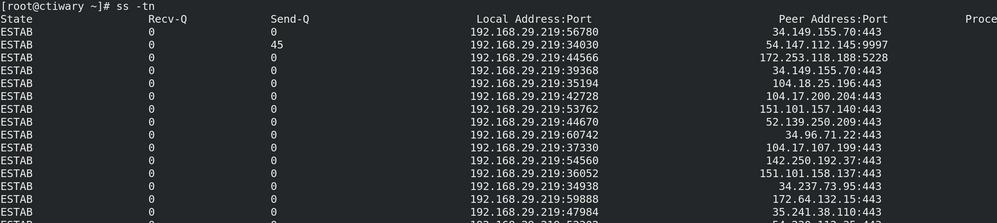
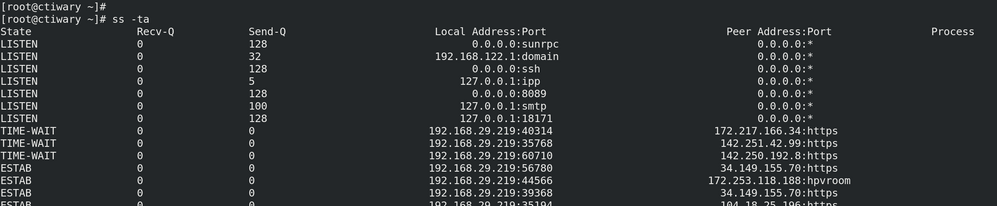
The -n option for the ss command does not impact IP address or how they're displayed - as evidenced by your output (and previously, mine).
In other words: in your output, if any of the IP address were impacted by the -n option, instead of displaying 192.168.20.219, they may appear as system1.lab.example.com. But this did not happen; all of the IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) were unchanged.
Instead, what changed were the port numbers, which were translated to service names.
Again, this is specifically stated in the man page for ss for -n. It makes no mention of IP addresses:
-n, --numeric
Do not try to resolve service names. Show exact bandwidth values, instead of human-readable.
Estrella Mountain Community College
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 1,976 Views
Ok sure ! Let me highlight this to the concerned development team and see what they have to say in this regard.
Red Hat
Learning Community
A collaborative learning environment, enabling open source skill development.