- Red Hat Community
- :
- Discuss
- :
- General
- :
- HTTP Response Codes: A Guide for Beginners
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,676 Views
HTTP Response Codes: A Guide for Beginners
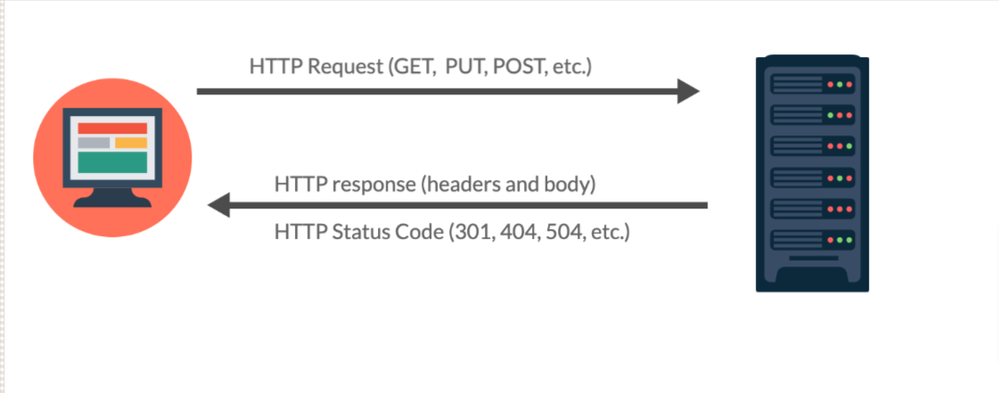
A server's reply to a client in response to an HTTP request is known as an HTTP response. It includes the resource being requested, its status, and any additional pertinent data.
The request-response model underlies all communications between your browser and a website. Your browser (client), which you use to access the internet, makes an HTTP request to the website server each time you put in an address, click on a link on a website, download a file, or carry out any other online operation. The server responds with an HTTP response after processing the request.
Three components make up the HTTP response messages:
The status line: This line contains information about the request's status, such as "200 OK" or "404 Not Found".
The heading fields are: These parameters include more details about the response, such as the resource's requested content type.
The message body contains, if any, the actual content of the resource that was requested.
You must have come through one of the below HTTP response codes in your day to day work :
200 OK: The request was successful.
400 Bad Request: The request was malformed or incomplete.
401 Unauthorized: The client is not authorized to access the requested resource.
403 Forbidden: The client is not allowed to access the requested resource.
404 Not Found: The requested resource does not exist.
500 Internal Server Error: The server encountered an error while processing the request.
503 Service Unavailable: The server is temporarily unavailable.
Basically HTTP error codes are three-digit codes that are divided into five classes:
1xx: Informational
2xx: Success
3xx: Redirection
4xx: Client Error
5xx: Server Error
Lets look at some of the important classes and responses :
- Successful responses :
- 200 OK : The request succeeded wheter it was HTTP GET , PUT , POST , TRACE method.
- 201 Created : Typical response after successful PUT or POST method.
- Redirection messages :
- 301 Moved Permanently : New URL which was moved to permanently is provided.
- Client error responses :
- 400 Bad Request : signifies that the client made an incorrect request to the server. There are several causes for this - required arguments were missing from the request, the request was illegible, a resource that doesn't exist was asked for in the request etc.
The sysadmin should examine the client's request first before attempting to resolve a 400 Bad Request issue. They should confirm that the request is formed correctly and contains all necessary parameters. If the request is valid, the system administrator should verify that the server is set up correctly to handle the request.
- 401 Unauthorized : signifies that the client does not have permission to access the requested resource. This may occur if the client's credentials are insufficient or if an access control list (ACL) is in place to safeguard the resource.
The sysadmin should confirm the client's credentials before attempting to fix a 401 Unauthorized error. They must confirm that the customer is logging in with the proper login and password. If the credentials are valid, the system administrator should confirm that the client has access to the resource by looking at its access control list (ACL).
- 403 Forbidden : signifies that access to the requested resource is not permitted for the client. This may occur if the resource is ACL-protected or if the client lacks the required permissions. Sysadmins should confirm that the client has permission to use the resource. The sysadmin should examine the client's rights if access to the resource is permitted for it.
- 404 Not Found: absence of the requested resource is indicated by this error code. This could occur if the resource was removed or the URL is wrong. sysadmin should inspect the server's file system to confirm that the resource is present before attempting to resolve a 404 Not Found issue. The system administrator should verify the URL to make sure it is accurate if the resource is real.
4. Server error responses:
500 Internal Server Error, signifies that the server had a problem while attempting to complete the request. There can be several causes for this like coding issue, faulty hardware or network issue.
The sysadmin should first examine the server logs before attempting to troubleshoot a 500 Internal Server Error. The logs will provide details about the error that happened. This data can be used by the system administrator to try and determine the error's root cause.
503 Service Unavailable: The server is momentarily unavailable, as indicated by the error code. This can take place if the server is busy or if it needs repair.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,572 Views
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- 5,570 Views
Really nice @Fran_Garcia !
Red Hat
Learning Community
A collaborative learning environment, enabling open source skill development.